Treatment for Pituitary Tumors in Israel

In 32% of patients from Eastern Europe who contact Top Ichilov for pituitary tumor treatment, Israeli physicians do not confirm this diagnosis.
The examination for pituitary tumors in Top Ichilov takes 3-4 days and costs $2,292.
Medications: dopamine agonists cabergoline and quinagolide, hormone therapy with somatostatin analogues – octreotide and lanreotide, pegvisomant.
Targeted therapy: antitumor drugs lapatinib (Tykerb) and temozolomide (Temodar).
Minimally invasive neurosurgery: transsphenoidal adenectomy.
Radiation therapy: stereotactic radiosurgery, Gamma Knife.
Pituitary tumor treatment in Top Ichilov is provided by a specialist team. It includes:
- A neurosurgeon – Professor Z. Ram;
- An endocrinologist – Professor Naftali Stern.
Pituitary Tumor Diagnosis In Israel
Day 1: Appointment with a Diagnostician
The patient is seen by Doctor I. Molchanov, the diagnostician. He takes the patient’s medical history and conducts a thorough physical exam. Afterwards, Dr. Molchanov compiles the patient’s health history in Hebrew for the Israeli specialists and refers the patient for further studies.
Day 2: Laboratory Tests and Imaging Studies

On this day, the patient undergoes the following procedures:
- Blood tests and urinalysis. The results of these tests show whether the patient suffers from insufficient or excessive hormone production.
- Brain imaging studies. A CT or MRI scan of the brain is used to determine the location and the size of the pituitary tumor (if the patient has brought a previously recorded MRI disk, Israeli physicians may conduct a revision; in this case, another MRI scan in Israel will not be required).
- Vision testing. This diagnostic procedure is used to determine whether the pituitary tumor has affected vision (including peripheral vision).
Day 3: Treatment Recommendations
The patient is seen by Professor Zvi Ram, the neurosurgeon. He informs the patient of the final diagnosis and offers a treatment program.
Duration of the examination: 3-4 days. Price: $2,292.
✓ Right Now: An opportunity to consult a Top Ichilov physician free of charge
It is important to correctly determine the type of the disease before starting treatment in the country of residence. Consult an Israeli physician right now, free of charge. Find out the prices for the necessary diagnostic procedures in Top Ichilov.
What Are The Advantages Of Pituitary Tumor Treatment In Israel?
- In Israel, minimally invasive surgery is widely used to remove tumors. Pituitary tumors in Israel are usually removed without any external incisions. Transsphenoidal surgery is carried out through the nostril.
- High proficiency of the Israeli neurosurgeons. A neurosurgeon’s professional training in Israel lasts for about 16 years. This period includes a university program and the long years of specialization during which the future expert masters the state-of-the-art brain surgery techniques.
Pituitary Tumor Treatment In Top Ichilov
Many pituitary tumors do not require treatment. If treatment is still needed, a Top Ichilov doctor will select therapy options corresponding to the type and size of the tumor and to the extent of brain involvement. The physician will also consider such factors as the patient’s age and overall health.
Treatment for the pituitary tumor patients is provided by a team of experts comprising a neurosurgeon, an endocrinologist, and a radiation oncologist. In order to treat the pituitary tumor and normalize hormone levels, doctors use such methods as surgery, radiation therapy and medications. These methods may be used either alone or in combinations.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of a pituitary tumor is usually required when the tumor compresses the optic nerve or produces certain excessive hormones. The success of surgery depends on the type, location and size of the tumor as well as extent of its spread into nearby tissues.
There are two main techniques of pituitary tumor surgery. These are:
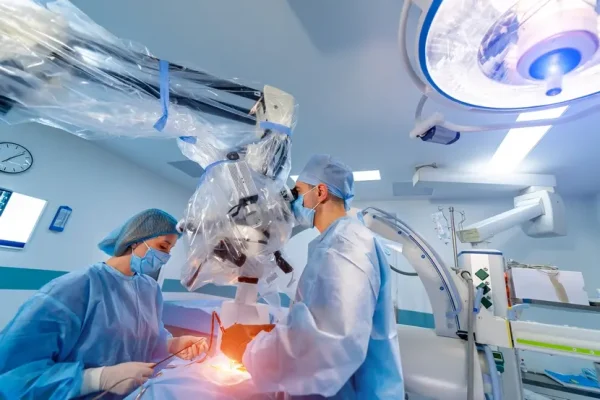
- Endoscopic transnasal transsphenoidal approach. This technique helps remove the tumor through the nose and sinuses without an external incision. Neither part of the brain suffers, and the patient has no visible scars afterwards. This technique, however, is not always suitable for larger tumors, in particular if the tumor has grown into nearby nerves or brain tissues.
- Transcranial approach (craniotomy). The tumor is removed through the upper part of the skull. Surgery is done through the incision in the scalp. This technique is used to remove large or complicated tumors.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation sources to destroy tumors. Irradiation may be used either after surgery or as a substitute for it if the patient is unable to have surgery. Radiation therapy also helps when the tumor is refractory or has recurred after surgery and causes symptoms that cannot be improved with medication. Possible radiation therapy options include:
- Stereotactic radiosurgery. Stereotactic radiosurgery is a way to deliver a single, high dose of radiation straight to the tumor with no incisions. Special brain imaging techniques are used to modify radiation according to the exact shape and size of the tumor. Healthy nearby tissues receive the least radiation and minimal damage.
- External beam radiation therapy. External beam radiation therapy is used to deliver small radiation doses to the tumor stage by stage. As a rule, radiation therapy is given on the outpatient basis. Sessions take place five days a week during 4-6 weeks. Notwithstanding the effectiveness of this approach, a few years may pass before the tumor stops growing and producing excessive hormones. Besides, external beam radiation therapy may damage the remaining healthy cells in the pituitary gland as well as healthy tissues of the brain, especially those close to the affected organ.
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). This type of radiation therapy uses a computer to shape the radiation beams and treat the tumor from various angles. The intensity of radiation may also be modified if necessary. This means that the tissues around the tumor will be less affected by radiation.
- Proton therapy. This is a type of radiation therapy that uses positively charged ions (protons) instead of X-rays. Unlike X-rays, a proton therapy session is stopped right after the delivery of a required radiation dose into the tumor tissues. The radiation is subject to highly-precise control and may be used to treat tumors with a lesser risk for healthy tissues.
The advantages and complications of any radiation therapy type are not evident. Sometimes, the effect becomes obvious only in a few months or years. A Top Ichilov radiation oncologist will assess your condition and discuss the advantages and drawbacks of each radiotherapy option with you.
Medications
Medications block excessive hormone production and, in some cases, help shrink certain pituitary tumors:
- Prolactin-Secreting Tumor (Prolactinoma)
The drugs cabergoline and bromocriptine (Parlodel) reduce the production of prolactin and, oftentimes, the size of the tumor. Possible side effects include sleepiness, dizziness, nausea, nasal congestion, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, confusion and depression. Some people who use these medications develop compulsive behavior – for instance, a propensity for gambling.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone-Producing Tumors (Cushing’s Syndrome)

Patients with Cushing’s syndrome and type 2 diabetes or glucose intolerance are recommended mifepristone (Korlym, Mifeprex). Mifepristone blocks the action of cortisol instead of reducing its production. Possible side effects include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, headaches, muscle pain, increased blood pressure, low potassium levels and swelling.
The newest medication for Cushing’s syndrome is called pasireotide (Signifor). It reduces the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone in the pituitary tumor. This drug is given by injection twice a day. Pasireotide is used if surgery proved ineffective or impossible. Side effects are rather common. They include diarrhea, nausea, high blood sugar, headaches, abdominal pain and fatigue.
- Growth Hormone-Secreting Tumors
Growth hormone-secreting tumors are treated with two types of drugs. These drugs are especially useful when hormone production cannot be improved surgically. One type is the somatostatin analogues comprising octreotide (Sandostatin) and lanreotide (Somatuline Depot). They reduce the growth hormone production and may shrink the tumor. They are given by injection, usually once every four weeks. Potential side effects of the somatostatin analogues include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dizziness, headaches and pain at the injection site. With time, most side effects decrease and even disappear completely. On the other hand, these medications may also cause gallstones and exacerbate the condition of diabetes mellitus patients.
The second type of drugs includes pegvisomant (Somavert). It prevents the excessive growth hormone from affecting the body. Injections are given daily. Some patients treated with this medication develop liver conditions.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
If the tumor or its surgical removal has reduced hormone production, you will probably need hormone replacement therapy to maintain normal hormone levels. Hormone replacement therapy is also given to some patients during radiation therapy.
Watchful Waiting
Watchful waiting (the wait-and-see approach, or delayed treatment) consists in regular examinations to check whether the tumor is growing. This option is suitable for pituitary tumors that do not cause any symptoms.
If the tumor causes no specific problems, treatment is usually not needed. Relatively young patients must understand that during watchful waiting, the tumor may change or grow. These changes sometimes require treatment. Together with the doctor, you will be able to evaluate both possible symptoms and potential treatment outcomes.
Advanced Treatment Options Implemented In 2024
The Use of Mass Spectrometry with Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption (MALDI MSI) in Pituitary Tumor Surgery
The MALDI MSI method differentiates the healthy pituitary gland tissues from the tumor within just 30 minutes. It helps determine the location of tissues containing excessive hormones and preserve as much healthy tissue as possible.
Mass spectrometry has already been used to detect tumors during surgery. Up until now, however, most attention was given to small molecules: metabolites, fatty acids and lipids. The new method helps assess hormone levels through protein analysis.
How To Receive Pituitary Tumor Treatment In Top Ichilov
- Call the clinic right now: +972-37621629
- Or fill in the form below. Our doctor will contact you within 2 hours.

Publication Date:














